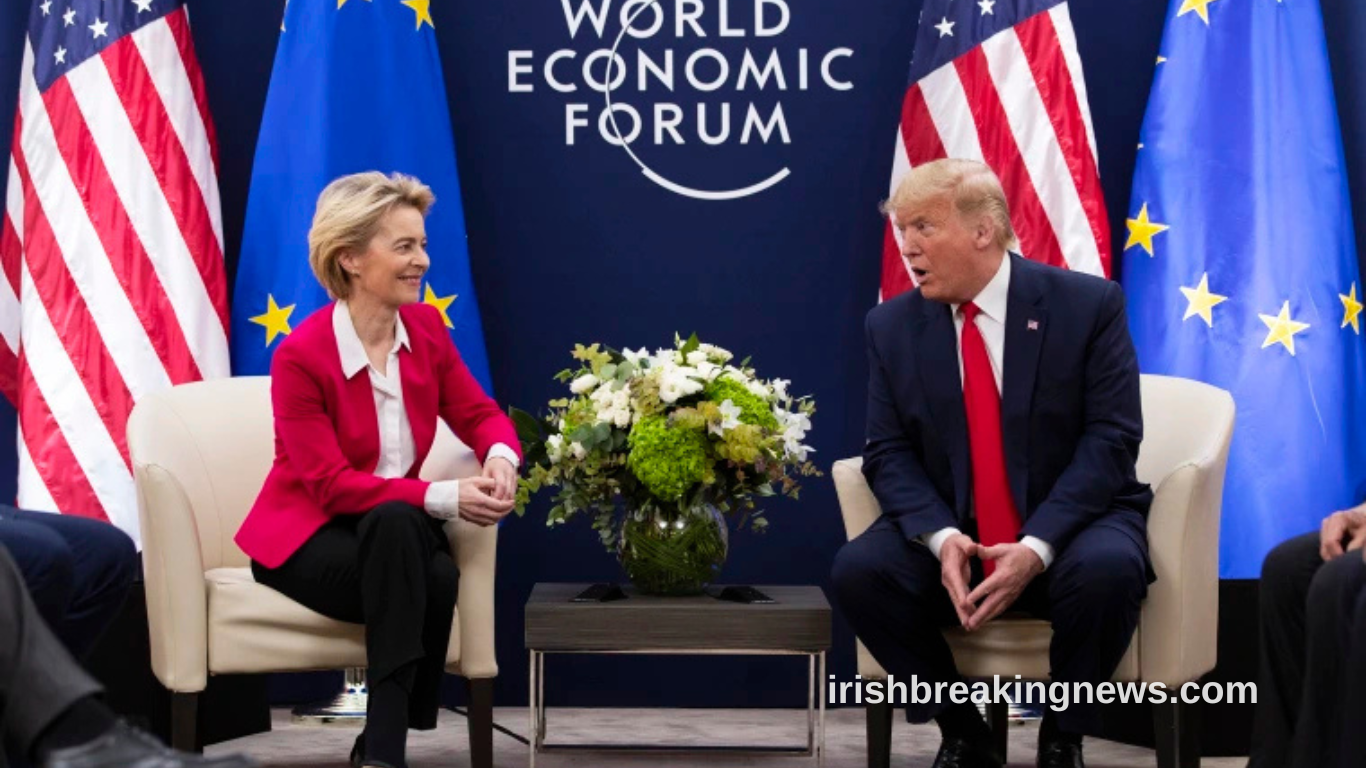
Recent developments in U.S. trade policy have reignited global concerns, especially across the Atlantic. Former President Donald Trump’s renewed calls for tariffs on European products have rattled diplomatic and economic circles, signaling a potential escalation in trade tensions. The implications could be far-reaching, disrupting economic stability and global supply chains.
The European Union, already navigating economic recovery challenges, now faces a looming threat that could impact key industries such as automotive, agriculture, and luxury goods. Trump’s aggressive stance on trade, rooted in a long-standing “America First” approach, challenges established economic alliances and risks retaliation from EU member states.
As both sides weigh their next moves, businesses, investors, and policymakers must prepare for a turbulent period. Understanding the stakes involved in this evolving scenario is critical for anyone tracking international trade dynamics or global economic health.
U.S. Tariff Threats Rekindle Transatlantic Trade Tensions
The idea of levying tariffs on European goods is not new. During his presidency, Donald Trump targeted various sectors, including steel, aluminum, and automobiles. His rationale emphasized the U.S. trade deficit and the need to protect American industries from what he considered unfair European competition.
Trump’s recent statements hint at reviving these protectionist policies. He argues that American manufacturers are at a disadvantage due to imbalanced trade deals. This rhetoric appeals to domestic industries but sends alarming signals to Europe. EU leaders interpret the move as economically coercive and politically antagonistic.
Read More : Crypto trader tortures man in NYC for Bitcoin theft
The potential targets include cars, wine, cheese, and high-end fashion products that form a significant share of EU exports to the U.S. Any implementation could trigger tit-for-tat measures, affecting U.S. exports like tech products, machinery, and agricultural goods.
Europe’s Response and Retaliation Readiness
The European Union has not remained silent. In Brussels, officials are already drafting countermeasures and signaling unity among member states. The bloc’s stance mirrors previous responses—firm, strategic, and measured.
During earlier tariff disputes, the EU imposed duties on American products such as Harley-Davidson motorcycles and bourbon. If Trump’s threats materialize, similar strategies will likely resurface, targeting politically significant American exports to pressure Washington.
Beyond tariffs, Europe may also leverage regulatory tools. Stringent compliance checks and delayed certifications for American firms could become part of the broader response. The EU’s extensive regulatory framework provides a soft-power mechanism to influence outcomes without immediate fiscal consequences.
Economic Impact on Key Sectors and Supply Chains
Tariffs don’t just affect government revenues; they ripple through entire economies. Industries heavily reliant on exports and imports stand to lose the most. For Europe, the automotive sector is a major concern. Germany, in particular, exports thousands of vehicles annually to the U.S. market.
In the U.S., agriculture could suffer due to restricted access to European consumers. Soybeans, dairy products, and meat exports could face retaliation, leading to reduced market share and falling farm incomes. Manufacturing and tech sectors may also feel the strain from rising component costs and disrupted logistics.
Global supply chains—already strained post-pandemic face added pressure. Tariffs introduce uncertainty, increase costs, and force companies to reassess sourcing strategies. Businesses might pass these costs to consumers, further fueling inflation concerns.
Political Ramifications Beyond the Economy
Trump’s tariff threats are not purely economic; they carry deep political undertones. Trade tensions can strain diplomatic ties and complicate cooperation on global challenges such as climate change, defense, and technology governance.
EU leaders prefer predictable trade relationships based on rules and mutual respect. Trump’s unilateral approach could hinder transatlantic collaboration and weaken NATO unity. Diplomatic disruptions could extend to multilateral platforms like the G7 and the World Trade Organization (WTO).
Within the U.S., the political fallout might polarize domestic opinion. While some support protectionism as a way to revive domestic industry, others warn it may isolate the U.S. from crucial allies. In Europe, leaders must navigate national interests while maintaining a unified EU front.
Global Markets React to Uncertainty
Financial markets respond swiftly to geopolitical shifts. Tariff threats often lead to volatility as investors reassess risks. Stock markets in both Europe and the U.S. may see fluctuations, especially in sectors directly affected by tariffs.
Currency markets also experience turbulence. Safe-haven assets like gold may see increased demand, while currencies such as the euro and dollar might fluctuate based on trade announcements. Investment in affected industries could slow down, delaying innovation and job creation.
Global confidence, already tested by inflation and geopolitical instability, could erode further if a trade war escalates. Restoring stability will require diplomatic finesse and a commitment to open dialogue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Trump proposing new tariffs on European goods?
Trump argues that European trade practices disadvantage U.S. industries, and tariffs are a way to correct trade imbalances.
Which European products are most likely to be targeted?
Luxury items, vehicles, agricultural products like cheese and wine, and fashion exports are high on the potential tariff list.
How might Europe respond to these tariffs?
The EU may impose counter-tariffs and regulatory delays or use legal channels through the WTO to challenge the U.S. moves.
What impact could this have on the U.S. economy?
Retaliation could affect American farmers, tech firms, and manufacturers by reducing exports and raising production costs.
How are global supply chains affected?
Tariffs increase operational costs, create delays, and encourage companies to diversify suppliers, complicating logistics.
Could this lead to a full-scale trade war?
Yes, if both sides escalate without compromise, a broad trade war affecting multiple sectors is likely.
Has the U.S. imposed tariffs on the EU before?
Yes, during Trump’s first term, tariffs were imposed on steel, aluminum, and other goods, prompting EU countermeasures.
Are there any diplomatic efforts to prevent this?
Talks are ongoing, but outcomes depend on the political climate and willingness of both sides to negotiate in good faith.
Conclusion
Trump’s renewed tariff threats against Europe introduce significant economic and political risks. The possibility of a transatlantic trade war could disrupt industries, destabilize markets, and strain long-standing alliances. Stakeholders must watch this evolving scenario closely, as its outcome could reshape global trade dynamics for years to come.